C 编程基础教程
作者:TeliuTe 来源:基础教程网
十、堆内存、 返回目录
堆内存可以动态分配所需的内存空间大小,而数组必须要在程序运行前指定空间大小,下面我们来看一个练习;
1、启动 Geany
1)点菜单“应用程序-编程-Geany”启动 Geany ,新建一个 c 源程序;
2)点菜单“文件-另存为”命令,以“heap”为文件名,保存文件到自己的文件夹;
2、分配堆内存
1)使用 mallac() 函数来获得需要的内存大小,它返回内存的起始地址,在开头先包含对应的库文件;
|
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> |
接着输入下面的代码,准备要用到的变量,第三个是指针变量,存放将来内存地址:
|
int i = 0; int a = 0; int *score = NULL; |
2)接下来输入一个数给 a,指定要申请的内存空间大小;
|
printf ("Input a number: "); scanf ("%d",&a); |
3)接下来申请内存大小,如果成功了,就把地址给 score 指针变量,否则给它的是“空” NULL;
| score = (int *) malloc(a * sizeof(int)); |
4)如果 score 不为空,就给它的各个单元赋值 i ,内存一般是连续的,可以当数组来使用;
|
for (i=0; i<a; i++) { score[i] = i; } |
5)赋值完毕以后,再显示一下各个单元的值;
| printf ("score[%d%s", a, "] = "); for (i=0; i<a; i++) { printf ("%d%s",score[i]," "); } |
6)使用完毕后,归还申请的内存,释放内存后,score 指针也应该让指向空 NULL;
|
free(score); score = NULL; |
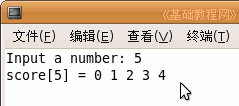
7)编译、生成、运行后,显示分配的内存单元和值;

|
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> int main(int argc, char** argv) { int i = 0; int a = 0; int *score = NULL; printf ("Input a number: "); scanf ("%d",&a); score = (int *) malloc(a * sizeof(int)); if (score != NULL) { for (i=0; i<a; i++) { score[i] = i; } printf ("score[%d%s", a, "] = "); for (i=0; i<a; i++) { printf ("%d%s",score[i]," "); } free(score); score = NULL; } return 0; } |
本节学习了堆内存使用的基本操作,如果你成功地完成了练习,请继续学习;
本教程由86团学校TeliuTe制作|著作权所有
基础教程网:http://teliute.org/
美丽的校园……
转载和引用本站内容,请保留作者和本站链接。